When alcohol is consumed, it is not processed by the stomach - instead, the liver is responsible for breaking it down into something easily expended by the body. The process by which the liver accomplishes this transformation is fairly simple, but surprisingly noxious.
H: Oxidation of Ethanol
Because ethanolEthanol is used in this discussion because it is the most common intoxicating agent. cannot be easily digested, the body converts it to acetic acid, which can be comfortably processed. This conversion is described by a two-step oxidation:
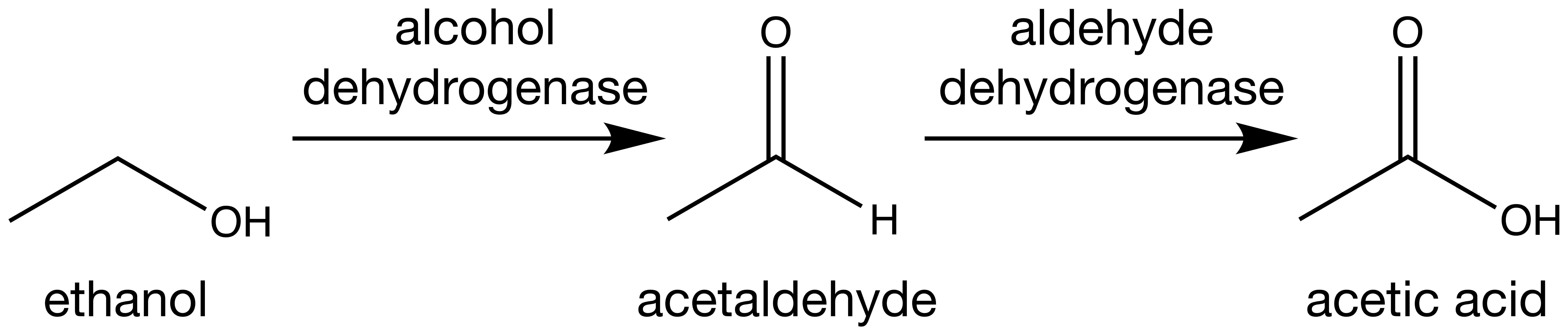
This reaction requires two enzymes: alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase. We will soon see why these are important! In the meantime, let us not ignore the intermediate of this reaction -
He: Acetaldehyde
As it turns out, acetaldehyde is responsible for many of the side effects experienced when consuming alcohol. Perhaps the most prominent and visible of these consequences is the alcohol flush responseOften referred to as Asian Glow or Asian Flush Syndrome., delineated by reddish blotches on the face and other parts of the body. Referral of this condition as Asian Glow actually comes from the fact that a disproportionate number of Eastern Asians experience the syndrome.
Why so?
Eastern Asians have a known genetic deficiency of aldehyde dehydrogenase, responsible for oxidizing toxic acetaldehydeNot only does significant amounts acetaldehyde cause facial flushing; it also induces nausea, headaches, is an irritant, and is a likely carcinogen. into expendable acetic acid. When excess acetaldehyde accumulates, either because of a deficiency of aldehyde dehydrogenase or because of an excess of alcohol dehydrogenaseAn excess of alcohol dehydrogenase causes ethanol to oxidize to acetaldehyde more rapidly than acetaldehyde can be oxidized to acetic acid., its toxic effects begin to impact the human body.
Li: Side-Side Effects
Ayaz,
You cry,
it can't be all bad... can it?!
It should be noted that formal research of this theory is currently developing, and there are is notable counter-evidence: for one, Native Americans are known to have an inordinately high rate of alcoholism, despite there being no enzymic differences between Native Americans and Whites.
No, it can't. Reports have shown that Eastern Asian populations also have a disproportionately low rate of alcoholism - the prevailing theory being that the unpleasant consequences due to a aldehyde dehydrogenase deficiency drives individuals against drinking more.